Understanding Business Models: A Comprehensive Guide
In today?s dynamic business environment, understanding business models is essential for anyone looking to thrive in the entrepreneurial world. Whether you are a startup founder, an established business owner, or an investor, having a strong grasp of what a business model is?and how it works?can be the key to success.
What is a Business Model?
A business model outlines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. It is the framework that explains how businesses make money and operate efficiently. While every company may have different goals and methods, all businesses depend on a robust business model to ensure profitability and scalability.
At its core, a business model answers these critical questions:
- What is the company’s value proposition?
- Who are its customers?
- How does the business make money (revenue streams)?
- What are its costs, and how are they managed (cost structure)?
The concept of a business model is often visualized through tools like the Business Model Canvas, a strategic template that simplifies the complex components into manageable blocks.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/businessmodel-85ce9a0a59e642cd941204a92ee873de.png)
“A great business model relies on finding the balance between customer needs and organizational efficiency.”
Key Components of a Business Model
Breaking down a business model into its main components allows us to understand the mechanics of how a company functions. These components include:
- Value Proposition
The value proposition explains what makes your product or service unique and why customers should choose your business over competitors. It directly addresses customer problems and presents your solution in a way that delivers value.For example, companies like Airbnb have created a compelling value proposition by providing affordable lodging options while connecting hosts with travelers in a trust-driven marketplace.
-
Customer Segments
Identifying your target market is crucial to the success of your business. No company can serve everyone, so understanding your ideal customer segments is key to focusing efforts and resources. Typically, businesses segment customers by demographics, geography, behavior, or needs.Successful companies tailor their business models to meet the specific demands of their chosen customer segments, ensuring a personalized customer experience.
-
Revenue Streams
How does your business make money? This is one of the most important questions a business model answers. Revenue streams can vary significantly between businesses:
- Subscription models (e.g., Netflix)
- One-time sales (e.g., retail)
-
Freemium models (e.g., Spotify)
Diversifying revenue streams can help mitigate risk and increase long-term profitability.
-
Channels
Channels refer to how a business delivers its product or service to its customers. This can include physical stores, e-commerce platforms, or third-party distributors. An optimized channel strategy ensures that your product reaches customers in the most efficient way possible, enhancing customer satisfaction.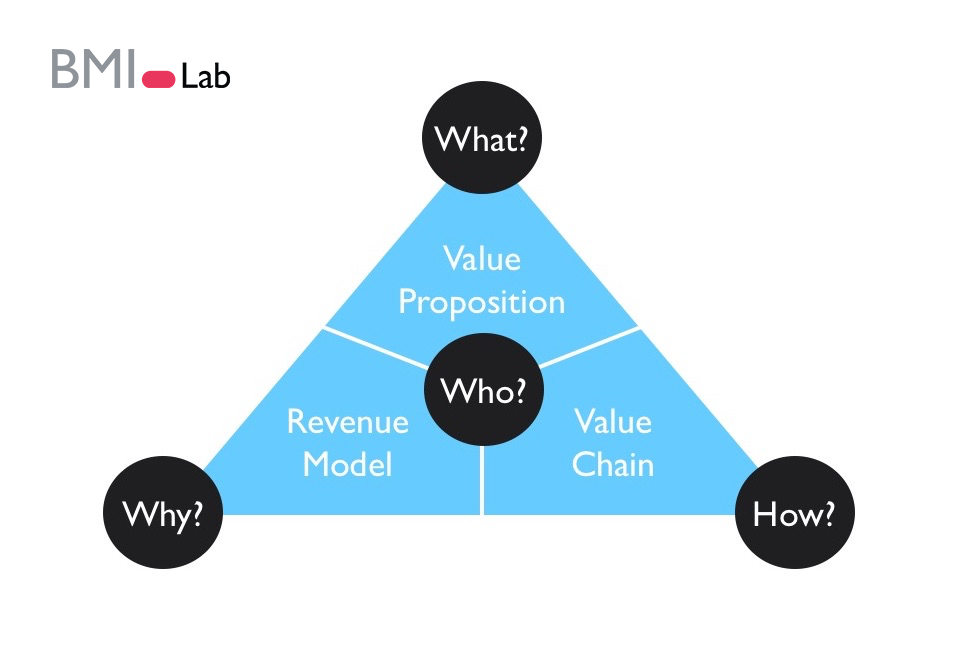
-
Cost Structure
The cost structure of a business model outlines the expenses required to operate. Fixed costs like rent and salaries, and variable costs such as raw materials, all play a role in determining whether a business can sustain itself profitably. Reducing unnecessary costs while maintaining product quality is often a fine balance that successful companies manage well.
Popular Business Model Types
Now that we’ve reviewed the key components of a business model, let’s explore some of the most popular business models used today:
1. Business-to-Business (B2B)
In a B2B model, businesses sell products or services to other businesses. Examples include software companies providing enterprise solutions, or manufacturers selling to wholesalers. B2B models often focus on building long-term relationships and recurring contracts.
Key Characteristics:
- Longer sales cycles
- Higher transaction values
- Emphasis on customer relationships and contracts
2. Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
B2C models represent companies that sell directly to consumers, such as retail stores, e-commerce platforms, or subscription services. This model often requires strong marketing strategies to attract and retain customers.
Key Characteristics:
- Shorter sales cycles
- Emphasis on customer satisfaction
- High volume of transactions

3. Subscription Model
The subscription business model has grown significantly in recent years, particularly in industries like software-as-a-service (SaaS), media, and fitness. Companies using this model charge customers a recurring fee (monthly or annually) in exchange for continued access to a product or service.
Examples:
- Netflix offers a streaming service based on monthly subscriptions.
- Adobe provides creative tools like Photoshop through a SaaS model.
Advantages:
- Predictable, recurring revenue
- Increased customer lifetime value
4. Freemium Model
In the freemium model, basic services or products are provided for free, while more advanced features require a paid subscription. This approach allows businesses to acquire a large customer base and convert them into paying customers over time.
Popular examples of the freemium model include apps like Spotify and Dropbox.
Advantages:
- Low barriers to entry
- Scalable, as more users upgrade to paid plans
5. Marketplace Model
The marketplace model connects buyers and sellers, acting as an intermediary platform. Think of companies like Amazon, eBay, or Uber. They don’t own the products or services they sell; instead, they create value by facilitating transactions between parties.
Advantages:
- Low inventory costs
- Scalable with technology

Importance of Business Models
Understanding your business model is fundamental to long-term success. It helps you identify the right strategies for growth, ensures that you can adapt to changes in the market, and clarifies your path to profitability. Without a well-defined business model, even the most innovative products can struggle to gain traction.
In an ever-changing landscape, businesses that continually refine and adapt their models are more likely to succeed.
Stay tuned for the second half, where we dive deeper into designing a business model, adapting to market changes, and examining real-world case studies of businesses that have excelled through innovative business models.
Designing a Business Model
Creating an effective business model requires strategic planning and a clear understanding of your market. Here are some essential steps to consider when designing or refining your business model:
1. Research and Analyze Market Needs
Before you develop your business model, conducting thorough market research is crucial. This includes understanding customer needs, market trends, and the competitive landscape.
- Identify Gaps: Look for unmet needs or inefficiencies in the market that your business can address.
- Conduct Surveys: Use surveys and interviews to gather insights directly from potential customers.
Resources like SurveyMonkey can assist in gathering this data effectively.
2. Develop a Value Proposition
Crafting a compelling value proposition is at the heart of a successful business model. Your value proposition should clearly articulate:
- What unique benefits does your product or service offer?
- How does it solve a problem for your target customers?
- Why should customers choose you over competitors?
An example of a strong value proposition is Spotify?s promise to deliver personalized music recommendations through its advanced algorithms, enhancing user experience.

3. Select the Right Revenue Model
Choosing the right revenue model is critical for ensuring financial viability. Consider the following options based on your business type and customer base:
- Direct Sales: Selling products directly to consumers or businesses.
- Subscription Fees: Recurring revenue through subscriptions (e.g., software, streaming services).
- Freemium: Offering basic services for free while charging for premium features.
Assess the pros and cons of each model to find the one that aligns best with your business strategy.
4. Establish Channels
Deciding how to reach your customers is vital. Different channels can include:
- Physical Stores: Direct interaction with customers.
- E-commerce Platforms: Online sales through your own website or marketplaces like Amazon.
- Social Media: Leveraging platforms to engage with customers and drive sales.
Selecting the right channels ensures that your customers can easily access your products or services.
Adapting Business Models to Market Changes
The business landscape is continuously evolving, influenced by technological advancements, economic shifts, and changing consumer behaviors. Here?s how businesses can adapt their models to remain competitive:
The Role of Innovation in Business Models
Innovation is crucial for business growth and sustainability. Companies must be willing to explore new technologies and methods to enhance their offerings.
- Case Study: Netflix transformed from a DVD rental service to a streaming powerhouse by embracing digital technology and altering its business model to focus on subscription-based services.
Leveraging Technology for Business Model Evolution
Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, big data, and automation can drastically alter how businesses operate. Utilizing these technologies can lead to:
- Improved customer insights
- Enhanced operational efficiency
- More effective marketing strategies
For instance, companies that utilize AI for customer service can provide quicker responses and a more personalized experience.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Developing Business Models
While developing a business model, avoid these common mistakes that can hinder growth:
- Ignoring Customer Feedback
Customer insights are invaluable. Regularly gather and analyze feedback to refine your offerings and enhance your business model. Ignoring this can lead to misalignment with customer needs. -
Overlooking Market Trends
Staying informed about market trends is crucial. Failing to adapt can render a business model obsolete. Regularly conduct market analysis to remain relevant. -
Neglecting Cost Management
Understanding your cost structure is vital. Businesses must keep an eye on expenses to maintain profitability. This includes both fixed and variable costs.
Case Studies: Successful Business Models
Examining successful business models provides valuable lessons. Let?s take a look at two notable examples:
Airbnb
Airbnb has disrupted the hospitality industry by creating a marketplace model that connects hosts with travelers. This innovative approach allows homeowners to monetize their unused spaces while offering travelers affordable lodging options.
Key Takeaways:
- Leverage technology to connect users
- Build trust through user reviews and ratings
- Adapt the model based on regulatory changes in different markets
Netflix
Starting as a DVD rental service, Netflix evolved into a global streaming giant by embracing a subscription model. Its commitment to investing in original content has set it apart in a highly competitive market.
Key Takeaways:
- Innovate continuously to meet changing consumer demands
- Utilize data analytics to personalize user experiences
- Adapt to market disruptions, such as the rise of competitors
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and developing a robust business model is essential for any company aiming for long-term success. A well-structured business model not only defines how a company operates but also highlights opportunities for growth and innovation.
As you embark on this journey, remember to keep customer needs at the forefront, remain adaptable to changes, and continuously refine your model for optimal performance. For further reading, you can explore resources like Harvard Business Review for insights on business strategy and innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a business model?
A business model defines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. It includes aspects such as the value proposition, customer segments, revenue streams, and cost structure.
2. Why are business models important?
They help businesses outline their strategies for making money, understand their customer base, and adapt to market changes, ensuring long-term sustainability.
3. What are some common types of business models?
Common business models include B2B, B2C, subscription, freemium, and marketplace models, each catering to different customer needs and market dynamics.
By employing the strategies discussed in this article, you can craft a business model that not only meets current demands but also adapts to future challenges.